Faster, Easier - METADATA
Less time and less typing to document project information
Metadata is critical to GIS data sharing. Without metadata, how do you know how the data was collected, what it can be used for, or how current it is? However, writing metadata for feature classes or other data created for a project can be a labor-intensive, time-consuming, and tedious process. Fortunately, using the ArcCatalog Metadata toolbar can streamline and speed the process of documenting your files. Before the ArcCatalog Metadata toolbar, when you had to document several datasets, you selected one of the files, opened the Metadata Editor in ArcCatalog, filled in the required fields, closed the editor, selected another file, and repeated the process.
Often, you entered the same characteristics over and over again. It doesn’t have to be that way. Just follow these steps.
1. When you begin to add metadata for a project, identify those characteristics common to all the project’s feature classes. These common items might be the project name and number, contact information for the organization, the project’s spatial reference information, and information on data access and use constraints.
2. Use one of the ArcCatalog metadata editors (e.g., FGDC ESRI, ISO) to create metadata for one of the project’s files, but enter only the characteristics you identify as common to all project data. Once this information has been entered, export the metadata just created to XML format by selecting the item in the ArcCatalog tree, clicking the Metadata tab in the right pane, and clicking the Export button on the ArcCatalog Metadata toolbar, then browse to the output folder and choose XML as the type of file to export.
3. This exported XML file, containing metadata common to all the files in your project, can be used to populate those metadata files for all project materials—feature classes, imagery, and maps. To add this metadata to a file associated with the project, select the file in ArcCatalog, click the Metadata tab, and click the Import XML button.
4. Repeat the process of importing this XML for every feature class or other file in the project.
5. Now open each feature class and complete the metadata by adding the information that is unique to that feature class (e.g., abstract, description, status, and keywords). This exporting/importing XML strategy will speed the process of adding metadata and eliminate much of the typing associated with this process. Remember, metadata can be created and attached in this manner to the maps, charts, and photographs associated with a project, as well as GIS datasets. Often, you entered the same characteristics over and over again. It doesn’t have to be that way.
Less time and less typing to document project information
Metadata is critical to GIS data sharing. Without metadata, how do you know how the data was collected, what it can be used for, or how current it is? However, writing metadata for feature classes or other data created for a project can be a labor-intensive, time-consuming, and tedious process. Fortunately, using the ArcCatalog Metadata toolbar can streamline and speed the process of documenting your files. Before the ArcCatalog Metadata toolbar, when you had to document several datasets, you selected one of the files, opened the Metadata Editor in ArcCatalog, filled in the required fields, closed the editor, selected another file, and repeated the process.
Often, you entered the same characteristics over and over again. It doesn’t have to be that way. Just follow these steps.
1. When you begin to add metadata for a project, identify those characteristics common to all the project’s feature classes. These common items might be the project name and number, contact information for the organization, the project’s spatial reference information, and information on data access and use constraints.
2. Use one of the ArcCatalog metadata editors (e.g., FGDC ESRI, ISO) to create metadata for one of the project’s files, but enter only the characteristics you identify as common to all project data. Once this information has been entered, export the metadata just created to XML format by selecting the item in the ArcCatalog tree, clicking the Metadata tab in the right pane, and clicking the Export button on the ArcCatalog Metadata toolbar, then browse to the output folder and choose XML as the type of file to export.
3. This exported XML file, containing metadata common to all the files in your project, can be used to populate those metadata files for all project materials—feature classes, imagery, and maps. To add this metadata to a file associated with the project, select the file in ArcCatalog, click the Metadata tab, and click the Import XML button.
4. Repeat the process of importing this XML for every feature class or other file in the project.
5. Now open each feature class and complete the metadata by adding the information that is unique to that feature class (e.g., abstract, description, status, and keywords). This exporting/importing XML strategy will speed the process of adding metadata and eliminate much of the typing associated with this process. Remember, metadata can be created and attached in this manner to the maps, charts, and photographs associated with a project, as well as GIS datasets. Often, you entered the same characteristics over and over again. It doesn’t have to be that way.
Just follow these steps.
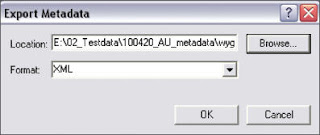
After filling in metadata items common to all files in the project, click the Export button on the Metadata toolbar in ArcCatalog and export the metadata in XML format.

No comments:
Post a Comment